Guide to Learning Project Management
Collaboration and Interpersonal Skills
Project success ultimately depends on people working effectively together. Emotional intelligence enables managers to navigate personality clashes and motivate diverse teams. They recognize that technical experts may communicate differently than business stakeholders, bridging these gaps through tailored facilitation. Conflict resolution skills transform disagreements into opportunities for better solutions rather than sources of dysfunction.
Stakeholder management requires ongoing attention beyond initial alignment. Regular check-ins surface changing priorities before they become crises, while demonstrating respect for each stakeholder's perspective builds trust reserves for challenging moments. Savvy managers map influence networks, identifying both formal decision-makers and informal opinion leaders who shape project perceptions.
Comprehensive diagnosis requires meticulous examination of all contributing factors. Just as medical professionals assess symptoms in context, project managers must evaluate challenges holistically rather than treating surface indicators.
Developing a Project Plan: A Step-by-Step Approach
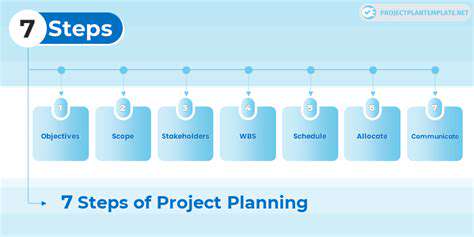
Defining the Project Scope
Creating a precise project boundary prevents scope creep's insidious effects. Effective scope statements specify both inclusions and exclusions, clarifying what the project won't address as much as what it will. Techniques like MoSCoW prioritization (Must have, Should have, Could have, Won't have) help teams focus on essentials when resources constrain ambitions. Scope validation with all key stakeholders early prevents painful renegotiations later.
Identifying Stakeholders
Stakeholder analysis should extend beyond obvious participants to include indirect influencers. Power/interest grids help prioritize engagement efforts, focusing intensive communication on high-power, high-interest individuals while monitoring others. Cultural mapping reveals potential alignment challenges when working across organizational silos or international borders. Early identification of potential opponents allows for proactive mitigation rather than reactive damage control.
Estimating Resources and Costs
Realistic estimation combines historical data, expert judgment, and contingency buffers. Three-point estimates (optimistic, pessimistic, most likely) account for uncertainty, while phased estimating allows refinement as projects progress. Resource leveling techniques prevent overallocation that burns out team members. Transparent cost breakdowns build credibility with sponsors, distinguishing between fixed costs, variable costs, and reserves for unknowns.
Developing a Timeline
Schedule development balances ideal sequencing with resource realities. Critical chain method protects the project timeline by adding buffers at strategic points rather than padding individual tasks. Progressive elaboration allows detailed near-term planning while maintaining flexibility for later phases. Visual timeline tools help teams understand how their work fits into the bigger picture, fostering ownership and accountability.
Defining Roles and Responsibilities
RACI matrices (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) clarify decision rights. Overlapping responsibilities create ambiguity while gaps lead to neglected tasks. Role definitions should specify not just deliverables but also decision authority levels and escalation paths. Cross-training key roles provides continuity when personnel changes occur mid-project. Regular role reviews ensure alignment as project needs evolve.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Effective risk management goes beyond identification to active response planning. Risk breakdown structures categorize potential threats systematically, while quantitative analysis assesses probability and impact. Response strategies should be tailored - avoiding some risks, transferring others, mitigating likely threats, and accepting residual risks consciously. Maintaining a living risk register that's reviewed regularly keeps the team prepared rather than surprised.
Monitoring and Controlling
Earned value management integrates scope, schedule and cost metrics for holistic tracking. Variance thresholds trigger predetermined responses, preventing small deviations from becoming major issues. Information radiators (dashboards, burn-down charts) make progress visible to all stakeholders. Regular retrospectives identify process improvements while there's still time to implement them in the current project.
Continuous Improvement and Project Closure
Continuous Improvement in Project Management
Ongoing enhancement transforms isolated successes into repeatable excellence. After-action reviews capture both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights, comparing planned versus actual outcomes across all knowledge areas. Improvement backlogs prioritize enhancement opportunities, balancing potential impact against implementation effort. Knowledge management systems prevent valuable lessons from being siloed with individual team members.
Defining Project Closure Criteria
Closure checklists ensure no loose ends remain. Formal acceptance criteria should be measurable and agreed upon in advance, preventing subjective disagreements at project end. Transition plans detail how deliverables will move from project teams to operational owners, including training and support requirements. Final quality audits verify all outputs meet specifications before sign-off.
Formal Project Closure Procedures
Structured closure rituals provide psychological and administrative completion. Final reports should highlight both achievements and improvement opportunities, serving future projects rather than just justifying past decisions. Contract closeout ensures all obligations are fulfilled and documentation archived appropriately. Celebratory events recognize team contributions, reinforcing positive behaviors for future collaboration.
Lessons Learned from Project Closure
Retrospectives yield maximum value when conducted at multiple project phases. Start, Stop, Continue frameworks structure constructive feedback, while anonymous input surfaces uncomfortable truths. Findings should be actionable rather than abstract, with clear owners assigned to implement agreed improvements. Sharing lessons across the organization prevents siloed learning and elevates overall capability.
Stakeholder Communication during Closure
Transition communications should address both rational and emotional needs. Success stories demonstrate return on investment, while honest assessments of challenges build credibility for future initiatives. Personalized thank-you messages acknowledge individual contributions beyond formal roles. Roadmaps showing how this project enables future work maintain momentum beyond the immediate effort.
Project Closure Documentation and Archiving
Thoughtful knowledge preservation balances completeness with accessibility. Metadata tagging enables future retrieval by multiple search dimensions (project type, technologies used, team members involved). Version control maintains integrity of final deliverables while preserving historical iterations for reference. Access controls protect sensitive information while making appropriate materials available organization-wide.
Project Closure Reporting and Evaluation
Final evaluations should measure against original baselines and evolving business needs. Benefit realization plans extend beyond project closure, tracking how deliverables create value over time. Sponsor satisfaction surveys provide candid feedback on management effectiveness. Team member assessments identify skill development and future placement opportunities, transforming project conclusions into career development moments.