Guide to Creating a Vertical Garden
Key Considerations
Evaluate your available space and sunlight exposure before selecting plants.
Match plant choices to your vertical garden's structural capabilities.
Develop a consistent watering schedule based on plant needs.
Select plants that complement each other's growth patterns.
Plan for ongoing maintenance to ensure long-term success.
Selecting the Perfect Vertical Garden System
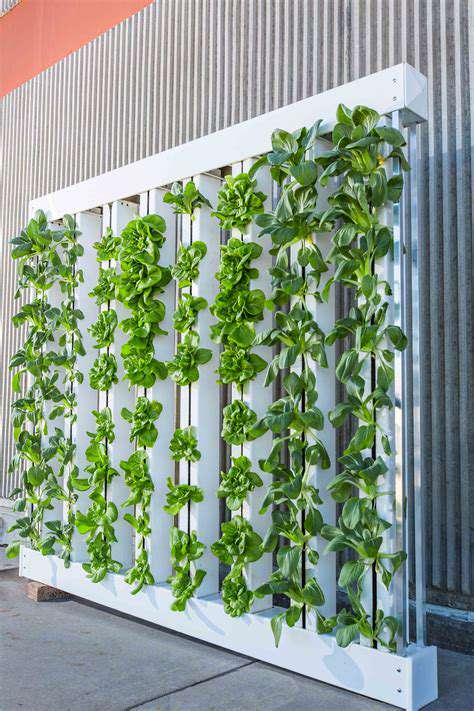

Essential Selection Criteria
The foundation of any successful vertical garden lies in choosing the appropriate system. Space constraints, aesthetic preferences, and maintenance requirements should all influence your decision. Before making a purchase, carefully measure your available area and consider how the garden will integrate with your existing decor.
Different environments demand different solutions. Urban balconies might benefit from modular panel systems, while spacious backyards could accommodate freestanding vertical planters. The system's material durability directly impacts its longevity, especially in outdoor settings exposed to weather elements.
System Varieties Explained
Modern vertical gardening solutions range from simple trellises to sophisticated hydroponic setups. Each type serves different purposes - some excel at showcasing flowering plants, while others specialize in vegetable production. The assembly complexity varies significantly between DIY options and pre-fabricated commercial systems.
Automated watering systems represent a game-changing innovation for busy gardeners. These setups maintain consistent moisture levels through integrated reservoirs and capillary action. While initially more expensive, they often prove cost-effective by reducing water waste and plant loss.
Strategic Plant Selection
Successful vertical gardens begin with thoughtful plant choices. Sun exposure represents the first critical factor - south-facing walls suit sun-loving species, while shaded areas require shade-tolerant varieties. The mature size of plants often gets overlooked but significantly impacts long-term success.
Consider growth patterns when selecting plants. Vining species naturally adapt to vertical spaces, while bush-type plants may need additional support. Proper spacing prevents overcrowding and ensures adequate air circulation between plants.
Ongoing Care Requirements
Vertical gardens demand consistent attention to watering needs. The vertical orientation causes faster moisture evaporation compared to traditional gardens, necessitating more frequent irrigation. Implement a regular inspection routine to catch pest issues or nutrient deficiencies early.
Seasonal adjustments prove crucial for maintaining plant health. Fertilization schedules should adapt to growth phases, while pruning maintains shape and encourages new growth. Winter protection measures may be necessary for perennial plants in colder climates.
Financial Planning
Vertical garden costs span a wide spectrum based on materials and complexity. Budget-conscious gardeners can repurpose materials like pallets, while premium systems offer advanced features like automated irrigation. Remember to factor in ongoing expenses for replacement plants, fertilizers, and potential system repairs.
The return on investment extends beyond financial considerations. Vertical gardens can increase property values, improve air quality, and provide fresh produce. These benefits often justify higher initial costs for quality systems.
Design Principles
Effective vertical garden design balances form and function. Color coordination creates visual harmony, while varied textures add depth and interest. Strategic plant placement maximizes light exposure for all species within the arrangement.
Consider viewing angles when designing your garden. Place showy specimens at eye level and reserve less ornamental plants for higher or lower positions. The garden should complement rather than overwhelm its surroundings.
Plant Selection Strategies for Vertical Spaces
Optimal Plant Choices
Vertical environments favor certain plant characteristics. Compact root systems, moderate growth rates, and attractive foliage make ideal candidates. Many herbs like thyme and oregano naturally thrive in vertical conditions, as do numerous flowering annuals.
For edible gardens, consider compact vegetable varieties specifically bred for small spaces. Cherry tomatoes, bush beans, and dwarf pepper varieties often outperform their full-sized counterparts in vertical setups. Strawberries make excellent choices for hanging pocket systems.
Light Adaptation
Light availability dictates plant selection more than any other factor. Accurately assess your site's light conditions throughout the day before choosing plants. Morning sun with afternoon shade suits many leafy greens, while fruiting plants typically require full-day exposure.
In low-light situations, consider supplementing with grow lights. Modern LED options provide energy-efficient solutions for indoor vertical gardens. Light meters can help quantify actual light levels for precise plant matching.
Water Management
Vertical gardens present unique watering challenges. Gravity causes faster drainage, potentially leaving upper plants drier than lower ones. Drip irrigation systems with multiple emitters help distribute water evenly throughout the structure.
Soil composition significantly impacts water retention. Incorporating water-absorbing polymers or moisture-retentive materials like coconut coir can reduce watering frequency. Always ensure adequate drainage to prevent root diseases.
Structural Considerations
The physical design of your vertical garden influences plant options. Lightweight systems suit small annuals, while sturdy metal frameworks can support small fruiting trees. Consider both the immediate and mature weight of plants when designing supports.
Modular systems offer flexibility to rearrange plants as they grow. This adaptability proves valuable when some species outgrow their initial positions. Planning for adjustability prevents future limitations.
Integrated Pest Management
Vertical gardens can either deter or attract pests depending on plant selection. Companion planting strategies help naturally repel common garden pests. For example, interplanting basil with tomatoes discourages whiteflies while enhancing flavor.
Regular monitoring catches infestations early when they're easiest to control. Physical barriers like insect netting often provide effective protection without chemicals. Beneficial insects like ladybugs can help manage aphid populations naturally.
Seasonal Planning
Rotating plant selections by season maintains year-round interest and productivity. Cool-season greens thrive in spring and fall, while heat-loving plants dominate summer months. Tropical plants can overwinter indoors in colder climates.
Succession planting ensures continuous harvests. As one crop finishes, immediately replace it with another suitable for the coming season. This approach maximizes vertical space utilization throughout the year.
Creating the Ideal Growing Environment
Soil and Medium Selection
The growing medium forms the foundation of plant health. Quality potting mixes designed for containers provide better results than garden soil. Soilless mixes offer excellent drainage while retaining sufficient moisture and nutrients.
Specialized vertical garden mediums often incorporate water-retentive materials. These products balance aeration and moisture retention in the unique vertical environment. Regular medium replacement (every 1-2 years) prevents compaction and nutrient depletion.
Efficient Irrigation Solutions
Automated watering systems provide consistency that manual watering often lacks. Drip systems with programmable timers allow precise control over frequency and duration. For larger installations, consider moisture sensors that activate watering only when needed.
Recirculating systems conserve water by capturing runoff for reuse. These closed-loop systems particularly benefit water-sensitive regions. Regular system checks prevent clogging and ensure even water distribution.
Microclimate Management
Vertical gardens create unique microenvironments. South-facing walls absorb and radiate heat, while north-facing ones remain cooler. Understanding these microclimates helps position plants according to their temperature preferences.
Wind exposure represents another critical factor. Tall vertical gardens may require windbreaks in exposed locations. Strategic placement near buildings can provide shelter while maximizing light exposure.
Nutrient Delivery Systems
Regular fertilization compensates for limited soil volume in vertical gardens. Slow-release fertilizers provide steady nutrition over several months. Liquid fertilizers offer quick correction of specific deficiencies when needed.
Organic options like compost tea improve soil biology while providing nutrients. Foliar feeding can supplement root uptake, especially for fast-growing plants. Always follow product instructions to prevent fertilizer burn.
Structural Integrity
Proper installation prevents future problems. Wall-mounted systems require secure anchoring to support the weight when fully planted and watered. Freestanding structures need stable bases to prevent toppling.
Regular structural inspections identify potential issues before failures occur. Look for signs of corrosion, wood rot, or loose fittings. Addressing minor repairs promptly prevents more significant problems later.
Aesthetic Maintenance
Regular grooming maintains visual appeal. Deadheading spent flowers encourages new blooms. Pruning controls size and shape while improving air circulation. Seasonal refreshes with new plants keep the display looking its best year-round.
Color coordination creates cohesive designs. Limit palettes to 2-3 dominant colors for visual harmony. Texture variation adds interest without overwhelming the senses.
Maintaining Your Vertical Garden
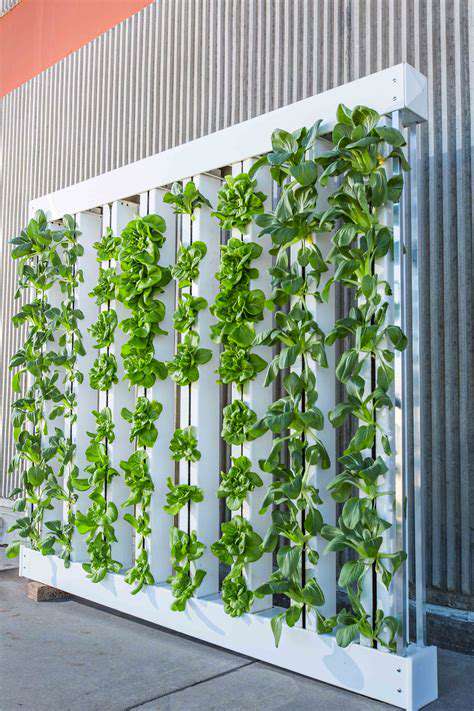

System-Specific Care
Different vertical garden systems require tailored maintenance approaches. Fabric pocket systems need occasional cleaning to prevent salt buildup. Modular plastic systems benefit from periodic disassembly for thorough cleaning.
Understanding your system's unique requirements prevents common maintenance mistakes. Manufacturer guidelines provide valuable insights into proper care techniques. Well-maintained systems often last several years longer than neglected ones.
Plant Health Monitoring
Regular inspections catch problems early. Look for discolored leaves, stunted growth, or pest activity. Early intervention significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Keep a garden journal to track plant performance and identify patterns.
Seasonal changes affect plant needs. Adjust watering frequency as temperatures fluctuate. Increase humidity for indoor gardens during winter heating seasons. Rotate plants periodically to ensure even light exposure.
Water Quality Considerations
Water source affects long-term garden health. Hard water leaves mineral deposits that can clog irrigation systems. Rainwater collection provides an ideal, chemical-free water source where possible.
Filtering tap water removes chlorine and other additives that may harm beneficial soil microbes. Letting water sit overnight allows chlorine to evaporate naturally. Water temperature matters - extremely cold water can shock plant roots.
Pruning Techniques
Proper pruning maintains plant health and appearance. Use clean, sharp tools to make precise cuts. Remove dead or diseased growth first, then shape as desired. Prune during active growth periods for fastest recovery.
Training vines and climbers creates desired patterns. Use soft ties that won't damage stems as they grow. Redirect wayward growth regularly to maintain the intended design.
Pest Prevention Strategies
Healthy plants naturally resist pests better. Ensure proper nutrition and growing conditions. Physical barriers like copper tape deter slugs and snails. Yellow sticky traps monitor flying insect populations.
Introduce beneficial insects before pest problems arise. Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites provide natural control. Neem oil and insecticidal soaps offer organic treatment options when needed.
Seasonal Transitions
Prepare gardens for seasonal changes. Fall cleanup prevents disease carryover to next season. Winter protection may include moving potted systems indoors or insulating roots.
Spring revitalization includes refreshing growing media and assessing system integrity. Summer care focuses on consistent watering and heat stress prevention. Each season brings unique maintenance priorities.







![Guide to Learning About [Specific Topic, e.g., Climate Change]](/static/images/31/2025-05/TheUnfoldingImpactsofaChangingClimate.jpg)