Guide to Learning About Economics
Understanding Consumer Behavior and Decision-Making Processes
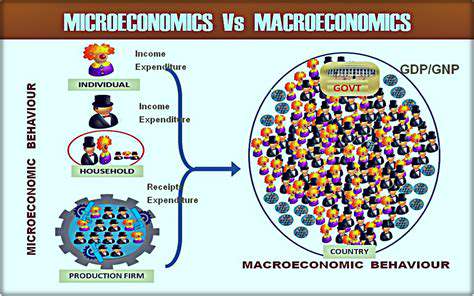
Consumer behavior sits at the heart of microeconomic analysis, revealing how people navigate purchasing decisions amid competing priorities. These choices don't occur in isolation - they're shaped by financial realities, personal tastes, and market prices, collectively weaving the fabric of demand. Businesses that grasp these patterns gain a competitive edge in crafting offerings that resonate with their target audiences.
People constantly weigh options to extract maximum satisfaction from limited budgets. This balancing act involves tough choices about what to prioritize, with each additional purchase bringing diminishing returns on enjoyment. The concept of marginal utility helps explain why consumers might pass on a fourth cup of coffee despite enjoying the first three.
Modern economic models acknowledge that people don't always act as perfectly rational agents. Behavioral economics demonstrates how cognitive shortcuts and emotional responses frequently override logical calculations, creating predictable patterns that businesses can anticipate.
The Role of Supply and Demand in Price Formation
Market prices emerge from the perpetual dance between what producers offer and what consumers want. When shoppers clamor for scarce products, prices naturally climb, signaling manufacturers to ramp up production. On the flip side, overflowing inventories prompt retailers to slash prices, tempting bargain hunters to clear the shelves.
The sweet spot where supply and demand curves cross represents economic harmony - the equilibrium where market forces naturally settle without external interference.
This delicate balance constantly shifts with technological breakthroughs, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer tastes. Companies that monitor these fluctuations gain foresight to adjust strategies before market tides turn against them.
Market Structures and Their Impact on Competition
Economic landscapes vary dramatically across industries, from bustling farmer's markets with countless identical vendors to utility sectors dominated by single providers. Perfect competition thrives when numerous small players offer indistinguishable products, keeping prices razor-thin through relentless efficiency.
Monopolies present the opposite extreme, where single firms dictate terms with little regard for consumer alternatives. Between these poles lie oligopolies - battlegrounds where a handful of corporate giants alternately collude and compete, keeping regulators vigilant for anti-competitive practices.
Recognizing these structural differences proves invaluable for policymakers crafting regulations that foster innovation while protecting consumer interests from potential abuses.
The Significance of Elasticity in Market Analysis
Elasticity measures how dramatically buying habits shift when economic conditions change. Some products, like premium electronics, see wild demand swings with minor price adjustments. Others, such as life-saving medications, maintain steady consumption regardless of cost fluctuations.
This sensitivity gauge helps businesses predict how price changes might affect their bottom lines. A thorough understanding of elasticity informs everything from promotional strategies to inventory planning, helping firms navigate turbulent markets.
Mastering elasticity concepts allows companies to anticipate how taxes, regulations, or economic shocks might ripple through their customer base.
Cost Structures and Production Decisions of Firms
Businesses constantly analyze their expense profiles to optimize operations. Fixed costs like equipment leases create financial bedrock, while variable costs ebb and flow with production volumes. The marginal cost - the price tag for making one more unit - becomes the critical factor in expansion decisions.
Initially, increasing output drives down per-unit costs through economies of scale. However, every factory eventually hits a point where adding more workers or machines yields progressively smaller gains. Savvy managers recognize this inflection point before resources get stretched too thin.
Strategic cost management separates thriving enterprises from struggling competitors, especially in industries where price wars constantly pressure profit margins.
Macroeconomics: Examining the Big Picture of the Economy
Understanding Aggregate Demand and Supply
Aggregate demand captures the total appetite for goods and services across an entire economy. This macroeconomic snapshot reflects combined spending by households, corporations, government agencies, and international buyers. Consumer optimism, business investment cycles, fiscal policies, and trade balances all contribute to this critical economic indicator. Tracking these components helps analysts predict economic expansions or contractions before they fully materialize.
On the production side, aggregate supply represents what domestic firms can profitably deliver at various price points. Input costs, technological capabilities, and regulatory environments all shape this supply curve. When these fundamental factors shift, they can alter an economy's productive potential and inflation trajectory simultaneously.
The Role of Government Policy in Macroeconomics
Public authorities wield powerful tools to steer national economies. Fiscal measures like infrastructure spending or tax reforms directly inject or withdraw economic fuel. Meanwhile, central banks fine-tune monetary conditions through interest rate adjustments and financial market operations.
These policy levers don't operate in isolation - their combined effects create complex economic feedback loops. Policymakers must carefully consider timing and magnitude when implementing interventions to avoid unintended consequences.
Analyzing Economic Growth and Development
Sustained economic expansion requires more than just temporary boosts - it demands continuous improvements in workforce skills, technological capabilities, and capital investment. Developing nations face additional hurdles like institutional weaknesses and infrastructure gaps that require targeted solutions.
The most successful development strategies address both economic metrics and human welfare indicators, recognizing that true progress transcends simple GDP figures.
Inflation and Unemployment: A Delicate Balance
The inverse relationship between price stability and job creation presents policymakers with persistent dilemmas. Stimulus measures that reduce unemployment often spark inflationary pressures, while anti-inflation policies may inadvertently increase joblessness.
Modern economies navigate this tension through sophisticated policy frameworks that attempt to maintain both price stability and maximum sustainable employment over business cycles.
International Trade and Globalization
Cross-border commerce creates complex interdependencies between national economies. Exchange rate fluctuations can suddenly make exports more competitive or imports more expensive, with cascading effects across industries.
Trade agreements establish rules that shape global supply chains and investment flows, creating both opportunities and disruptions for domestic producers. Navigating this landscape requires understanding how currency movements, trade policies, and global demand patterns interact.
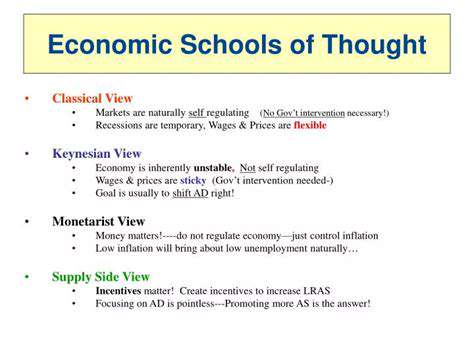
Exploring Different Schools of Economic Thought
Deep Ecology
Deep ecology challenges conventional thinking by asserting that all life forms possess inherent value beyond human utility. This philosophical approach rejects hierarchical views of nature, instead emphasizing humanity's role as one thread in Earth's intricate web of life.
This perspective demands radical rethinking of environmental policies, moving from resource management to recognizing nature's intrinsic rights. Implementing such principles would transform everything from urban planning to agricultural practices.
Ecofeminism
Ecofeminist analysis reveals disturbing parallels between societal structures that subordinate women and economic systems that exploit nature. Both patterns stem from cultural narratives that valorize domination and control over nurturing and sustainability.
By exposing these connections, ecofeminism provides powerful critiques of development models that sacrifice both gender equity and environmental health.
Social Ecology
Social ecology traces environmental degradation to underlying social hierarchies and power imbalances. This school argues that truly sustainable societies require dismantling oppressive structures that separate human communities from natural systems.
The movement advocates for grassroots democracy and local self-sufficiency as antidotes to both social injustice and ecological crisis.
Environmental Ethics
Environmental ethics systematically examines moral obligations toward non-human entities and future generations. This field grapples with difficult questions about animal rights, biodiversity preservation, and intergenerational equity.
These ethical frameworks help societies navigate trade-offs between economic development and environmental protection.
Environmental Justice
Marginalized communities worldwide disproportionately bear environmental burdens while receiving few benefits. Environmental justice movements highlight how race, class, and geography determine exposure to pollution and access to natural resources.
Addressing these disparities requires policy approaches that recognize environmental quality as a fundamental human right.
Post-Normal Science
Traditional scientific methods struggle with complex environmental challenges involving high uncertainty and conflicting values. Post-normal science advocates for inclusive decision-making that incorporates diverse knowledge systems and stakeholder perspectives.
This approach acknowledges that solving environmental problems requires more than technical expertise - it demands democratic deliberation.
Land Ethics
Aldo Leopold's land ethic proposes a moral framework where humans act as responsible members of biological communities rather than conquerors of nature. This philosophy emphasizes stewardship over exploitation and long-term sustainability over short-term gain.
Implementing land ethics would fundamentally transform how societies value and interact with natural systems.